| PMC full text: | Published online 2014 Nov 18. doi: 10.3390/nu6115184
|
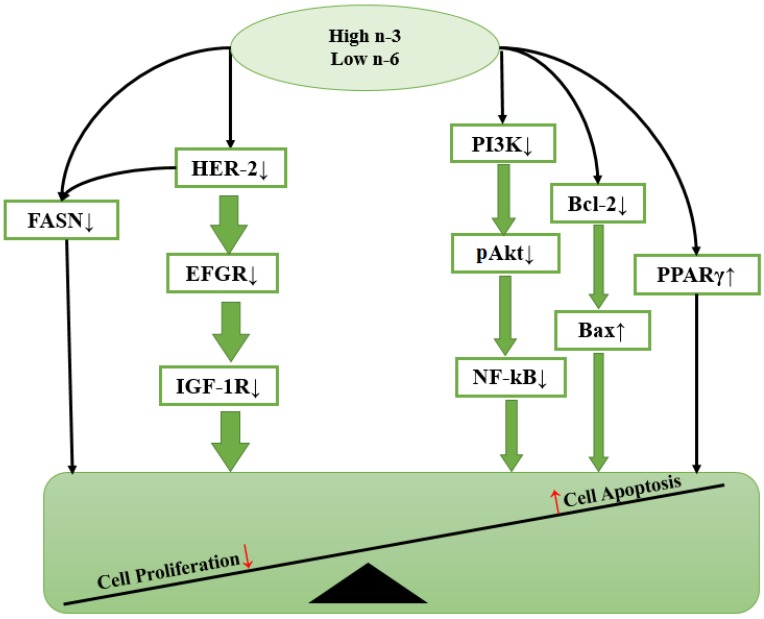
Figure 2
Hypothetical scheme showing how n-3 PUFA modulates cell functions via intracellular signaling molecules. Cell proliferation and cell apoptosis are the two important fundamental processes integral to carcinogenesis. n-3 PUFA exerts anti-cancer effects by reducing the expression of some growth factors including human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and insulin-like growth factor 1(IGF-1R); inhibiting cell proliferation by either activating PPARγ or decreasing levels of fatty acid synthase (FAS) protein; and promoting cell apoptosis via blocking PI3K/Akt pathways, downregulating phosphorylated Akt, inhibiting NF-κB activity and lowering Bcl-2/Bax ratio.