

Effect of an Online, Mobile App-mediated Structured Meal
Replacement Program on Weight Management:
Outcomes in a Real World SettingThis section is compiled by Frank M. Painter, D.C.
Send all comments or additions to: Frankp@chiro.org




FROM: ObesityWeek 2014 ~ FULL TEXT
Francis C. Lau, PhD, FACN; Bruce P. Daggy, PhD, FACN and Jamie F. McManus, MD, FAAFP
Shaklee Research Center,
Pleasanton, CA
Why was this study done?
The prevalence of overweight and obesity has grown into a worldwide epidemic in recent years. Currently, more than two in three adults are either overweight or obese. This study was designed to understand the effects of a structured meal plan and a mobile app on weight management.
What This Study Found
Average weight loss after 13 weeks following the program was 12.1 pounds (approximately 4 pounds a weeks). Twenty percent (30 out of 146) of obese participants reduced their BMI below 30 by the end of the study and were reclassified as overweight (and not obese).
From the Full-Text Article:
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
The prevalence of overweight and obesity has grown into a worldwide epidemic in recent years. Currently, more than 2 in 3 adults are either overweight or obese. Obesity is a risk factor for diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, osteoarthritis, and certain cancers including colon cancer and breast cancer. As a result, obesity significantly decreases the quality of life and life expectancy. The global socioeconomic burden imposed by obesity and its related comorbidities is tremendous.
In order to combat the obesity epidemic, an increased effort has been devoted to developing commercial products, diets, services, and programs to support weight loss and prevent weight gain.
Structured meal replacement programs consisted of optimized macronutrient composition and easily accessible motivational support have been shown to promote weight loss by providing convenient alternatives to the typical high fat, hyperglycemic, and supersized American diets.
This research was designed to evaluate the effects of a commercially available, mobile app-assisted, structured meal replacement program on weight loss. The diet plan consisted of 2 hypocaloric, high protein, clinically verified low glycemic index meal replacements and snacks, plus one self-prepared meal based on recipes provided. The meal replacements contain supplemental free leucine based on studies showing that could help maintain lean body mass.
METHODS
Study design:
Time-series observational study.
Subject population:
Customers who purchased commercially available meal replacement kits (Shaklee 180) and signed up for an online mobile app to track their body weight while they were on the meal replacement program.
Data collection:
Weekly data were collected on individuals reporting their body weight via mobile app for 13 weeks (3 months), approximately 13% of all users who signed up for the program. Diet program: two meal replacements, snacks between meals plus a self-prepared meal daily.
Diet program:
Two meal replacements, snacks between meals, plus a self-prepared meal daily.
Meal replacements:
Low-glycemic shakes and/or meal bars each providing approximately20–24 g of protein,
3–7 g of fat,
30–37 g carbohydrate,
6–7 g of fiber, and
23 vitamins and minerals for a total of 260–270 calories per serving.Snacks contain
6–10 g of protein,
2–3 g of fiber, and
100–140 Calories per serving.Self-prepared meals:
Recipes were included in the meal replacement kits and were also available online. Typically meals consist of4 oz. protein from skinless chicken, pork tenderloin or lean beef;
1 cup of steamed vegetables;
a small serving of carbohydrate such as a small baked potato, 1/3 of a cup of brown rice or a 6” tortilla;
a small salad of healthy leafy greens with low-calorie dressing.Online support:
Online tools and mobile app providing information on daily caloric intake, recipes, exercise programs, etc. were readily available to motivate participants.
Statistics:
Weekly data were normalized by baseline transformation. Two-tailed t-test was used for baseline comparison at specific time points and ANOVA was used for comparisons among different time points. P-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
See the Tables and figures below.

Table 1

Figure 1

Table 2
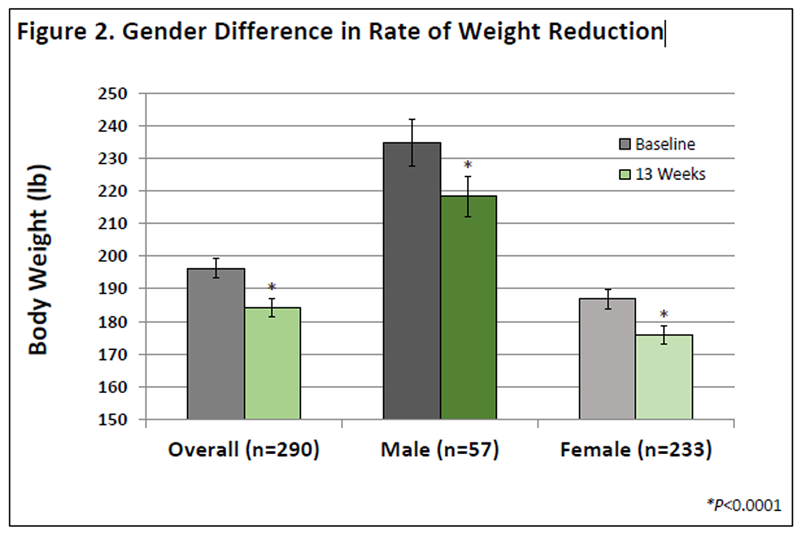
Figure 2
SUMMARY
Significant reduction in body weight by 12.1 lb (6.1% of initial body weight) after 13 weeks (Figure 1)
Significant reduction in BMI by 1.91 kg/m2 after 13 weeks (Table 2)
Significant weight loss was observed as early as after 1 week resulting in an average of 2.7 lb weight reduction (Figure 1)
Gender-stratified analysis showed that men lost significantly more weight than women (-16.5 lb vs. -11.0 lb or -7.0% vs. -5.9% of their initial body weight) (Figure 2)
Categorical shift occurred such that 30 out of the 146 obese participants had a BMI < 30 at the end of 13 weeks (Table 2)
CONCLUSIONS
Shaklee 180 structured meal replacement program promoted a healthy and clinically meaningful weight loss in a relatively short time frame. People on this diet program lost an average of 4.0 lb per month over 3 months.
Potential limitations associated with the current study include possible errors from self-reported data. Additionally, the data presented here consisted of subsets of cross-sectional results at specific time points which might not represent the whole population of users who initially signed up for the program.
Longitudinal studies are warranted to evaluate the effects of this program on weight loss maintenance over an extended period of usage.

Return to SHAKLEE STUDIES
Since 12-11-2015


| Home Page | Visit Our Sponsors | Become a Sponsor |
Please read our DISCLAIMER |