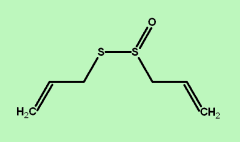
 | AllicinMW: 127.27
Formula: C6H10OS2 |
What is Allicin?
Allicin is garlic's defence mechanism against attacks by pests. When the garlic plant is attacked or injured it produces allicin by an enzymatic reaction. The enzyme alliinase, converts the chemical alliin to allicin, which is toxic to insects and microorganisms. The antimicrobial acivity of allicin was discovered in 1944 by Cavallito. Purified allicin is not sold commercially because it is not stable and has an offensive odour. Allicin extracted from garlic loses its beneficial properties within hours and turns into other sulphur containing compounds. Diallyl trisulfade, which is similar to allicin but is chemically produced, is stable and is used for treatment bacterial, fungal and parasitic infections.
Distribution
Allicin is the predominant thiosulfinate in garlic (Allium sativum).
Allicin is the chemical responsible for the typical and offensive odor of garlic.
Health Benefits of Allicin
Allicin, one of the sulfur compounds of garlic, possesses antioxidant activity and is
shown to cause a variety of actions potentially useful for human health. Allicin exhibits hypolipidemic, antiplatelet, and procirculatory effects. It demonstrates antibacterial, anticancer and chemopreventive activities. In addition, aged garlic extract possesses hepatoprotective and neuroprotective. But a factor that will limit the biological activity of allicin is its instability. Fresh crushed garlic cloves generated antibacterial activity and chemically detectable allicin, but this activity declines on a daily basis in aqueous and ethanol solutions. Allicin is also not bioavailable and will not get absorbed in the blood, even after ingesting large amounts of allicin.
Antimicrobial
The antimicrobial effect of allicin is due to its chemical reaction with thiol groups of various enzymes.
The phytochemical inhibits bacteria and viruses, but also yeasts such as candida. By its antimicrobial activity, allicin may be an effective therapeutic candidate to promote ulcer healing. In vitro-studies have demonstrated the antimicrobial activity against various pathogens, such as Helicobacter pylori, Staphylococcus aureaus, Escherichia coli and Lancefield group B streptococci.
Anticancer
In vitro studies show that allicin inhibits the invasion and metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells. The phytochemical also exhibits antigenotoxic action. But the anticancer effect of allicin in humans remains uncertain, because of its low stability and poor bioavailability.
Heart health
Garlic has been suggested to improve heart health by lowering blood pressure, but scientific studies have provided conflicting results. One study showed that the protective role of allicin against atherosclerosis, is not only the direct result of its antioxidant activity but also of other mechanisms, such as lipoprotein modification, inhibition of LDL uptake and degradation by macrophages.
Research Reviews
Intake of Garlic and its Bioactive Components
The influence of heating on the anticancer properties of garlic.
Pharmacologic activities of aged garlic extract in comparison with other garlic preparations.
Synonyms
Diallyl thiosulfinate
| 
